This is present in every company, it is what the company stand for and what they believe in. The culture of a country gives it its identity, just like the culture of a company gives it its identity.
Organisation culture is "the way we do things around here" (Deal & Kennedy, 1982).
It is "a body of learned behaviour, a collection of beliefs, habits and traditions, shared by a group of people and learned by people…." (Hofstede, 1984).
The organisation culture must be accepted by new employees, if they cannot do that they will leave. It is very hard to put into writting each company's individual culture but it influences the mentality and personality of the work force.
To talk about the visual and formal sides of organisation culture I will use French's and Bell's (1990) Organisational Iceberg model.
 - This top layer of the iceberg, at which only about 10% of the iceberg is exposed, lies the visable and formal part of the iceberg.
- This top layer of the iceberg, at which only about 10% of the iceberg is exposed, lies the visable and formal part of the iceberg.- Here below the surface of the water lies the other part, this part consists fo 90% of the iceberg yet it is concealed from view.
The visable formal organisation consists of;
Goals
Strategy
Structure
Systems and Procedures
Products and Services
Financial Resources
Management
Goals
Strategy
Structure
Systems and Procedures
Products and Services
Financial Resources
Management
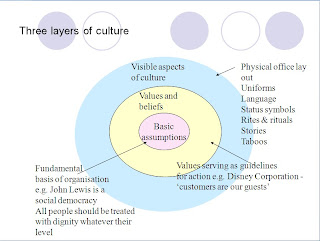
The idea that the visable aspect of organisation culture is different to the rest was also used by Shein (1992) with his layer principle.
Visual/formal culture
Goals - Mcdonalds had many adverts for "Happy meals" and "Student offers", this suggests their goals are to provide a value for money environment for children and young students. Also their staff were friendly and made sure the customer was satisfied therefor another goal my be to satisfy their customers.
Strategy - Due to the amount of deals and offers their strategy appears to be to sell groups of product for a reduced price rather than selling individual products for a higher profit. This provides the customer with a feeling that they food is less expensive, which it is, meaning they will go there more oftern and also buy more when they are there.
Structure - During the research visits Mcdonalds seemed to have one or two managers that overlooked the rest of the staff. One would look after the cashiers and the other made sure the cooks were working efficiently.
Systems and Procedures - There wasn't any visable evidence of systems or procedures.
Products and Services - As mentioned earlier there seemed to be a strong emphasis on the selling of products in a packages i.e. meals and offers. Also as mentioned earlier the service was good and it seemed as though the workforce were very concentrated on keeping the customer happy.
Financial Resources - The Mcdonalds used for this research was about average size, it was clean with sufficient staff to tackle customers and it also had sufficient seating and eating space. From this it seems that Mcdonalds has good financial resources and are not wasting them.
Management - This seemed sound as the employees were working well and efficiently and there were no long waits for food or orders. At one point there was a dissagreement between the manager and a worker, the manager wanted the worker to "Welcome" each customer and was very loud when the employee failed to do so, other than that it seemed like great management.
Uniform - Due to the uniform there was a clear indication of who did what job. The uniforms were split into cashiers, cleaners, cooks and the two managers.
In 1993 Handy introduced his idea of the four types of culture.
They consisted of Power culture
Role culture
Task culutre
Person culture
Power Culture
The power culture is common in small businesses. The main idea behind the power culture is very authoritarian, it basically suggests that there is one focal leader, this leader is given all power and he/she has the control over everything in the business.


Role Culture
This culture relies strongly on framework and hiearachy. The structure of this strongly resembles that of a Greek temple. Hierachy dominates this culture, instructions and orders are sent from the top of the pyramid to the bottom, the bottom sent information back up to the top.
This type of culture may be used in
Top Management
] [
] [
\ /
\/
Personel Production Finace Marketing
Task culture
Organisations with substantial amount of profect based operations tend to use this culture i.e. civil engineering or consultancy. It relies heavily on team work and linking between the whole organisation. Decision making is usually a group task in task culture.
Person culture
A typical organisation for this culture is a consultancy or a barrister's chambers. It is similar to the power culture because it involves one person to be the focal point but in person culture this role is changed for specific tasks so that there is a different person acting as the focal point for each task.
It is difficult to classify any business culture clearly into one of these types of culture because today more and more businesses adapt to what is required of them to survive. Many businesses use a mixture of three or all of these types of cultures which makes it difficult to decide which one is the predominant one. Also there may be several of these cultures active in one business for example a power culture may be used in one department and a person culture in another yet they are still in the same organisation.
Overall it is my opinion that culture plays a very strong part in an organisation but it is very difficult to classify which one is in use all the time because there are many organisations that use a multitude of these at once.
References
Martin, J. (1998), "Organizational Behaviour and Management", 3rd ed, London: Thomson

A very good blog. You have missed out the final element, which includes linking to a company who you believe has a strong culture. You can add this to the blog at any time. Well done!
ReplyDelete